| Home | Strategy | Activities | Grants | Publications | People | Sponsors | Contact Us | ||||||||||||||||
José Luis Vázquez-Poletti - Students
Home | Publications | Teaching | Students | El Escorial | Capoeira | Ham Radio
 “It's not only education but ideas that will help you survive outside this classroom.”
“It's not only education but ideas that will help you survive outside this classroom.”
As vectors of the Future, students need the best technology to bring their incredible ideas to reality while complementing their education. Distributed computing paradigms and in particular cloud computing are a great choice due to their high accessibility and the availability of open source tools. Basically, they open up a world of research possibilities and engenders a fast learning process, allowing the students to develop in a reasonable time projects like the ones that are outlined below.
2024-2025
D(AI)mos
Authors: Nieves Núñez Ugena and Albert Luque Fernández (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Engineering (UCM) co-advised with David Pacios Izquierdo.
Description: The project focused on designing the methodology rather than delivering a complete tool. It analyzes each step and requirement necessary to build such a system. Routers are critical components in any network—from home environments to enterprise edge devices—so securing them is essential to prevent attacks on downstream devices. This methodology evaluates the security configuration of a router and outlines potential vulnerabilities along with recommended fixes.In the end, the project highlights the importance of having a large, high-quality dataset. Such data is vital for improving model performance and generating accurate, actionable results.
Serverless Computing Architecture for Medical Data Classification
Authors: Martín Corchuelo Verjano (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Engineering (UCM) co-advised with Juan Antonio Clemente Barreira.
Description: The objective of this project is to develop a cloud-based application capable of accurately predicting breast cancer from tumor measurement data. Breast cancer is still one of the deadliest diseases affecting women worldwide, emphasizing the need for precise and accessible early detection tools. By taking advantage of the advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly supervised machine learning algorithms allowing users to quickly and reliably classify tumors as benign or malignant through a straightforward online interface. This entire system is developed using cloud-based technologies, ensuring scalability, security, and low operational costs. While it is designed to be accessible to everyone, it is primarily intended for use by healthcare professionals.
CylonNet
Authors: Lucas Calzada del Pozo (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Engineering (UCM) co-advised with David Pacios Izquierdo.
Description: Set in the Battlestar Galactica universe, this research introduces CylonNet, a modular web platform designed to enhance practical cybersecurity education through hands-on, gamified learning. Aimed at Computer Engineering students at the Complutense University of Madrid, the platform offers a catalog of community-created vulnerable laboratories, each deployed in isolated Docker containers. Users are challenged to exploit these intentionally insecure environments, capture embedded flags as proof of successful attacks, and submit them for automatic validation. A ranking system rewards progress with experience points and visible user levels, fostering engagement and competition. Fully containerized with Docker Compose, CylonNet ensures scalable, reproducible deployment across diverse systems, offering an accessible and impactful tool for cybersecurity training.
Optics and Processing of QR Codes Through Chromatic Encryption in Distributed Systems
Author: Sara Ignacio Cerrato (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: PhD Thesis in Optics (UCM), co-advised with José Miguel Ezquerro Rodríguez and María Estefanía Avilés Mariño.
Description: This study explores methodologies to enhance both the encryption and storage capacity of QR codes. By leveraging the unique properties of color channels (red, green, blue, and alpha) the research employs multiplexing and cryptographic techniques to significantly improve data security and increase the amount of information that can be stored within a single QR code. Additionally, the study investigates advanced encoding methods based on complex patterns, enabling the secure storage and transmission of high-density data across distributed computing environments.
2023-2024
Optimization of applications through serverless computing architectures
Author: David Pacios Izquierdo (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: PhD Thesis in Computer Architecture (UCM), co-advised with Jorge Jesús Gómez Sanz.
Description: This research delves into the transformative potential of serverless computing in the realm of data management, emphasizing its significance in enhancing operational efficiency and user convenience in the modern digital landscape. By leveraging the paradigm of automatically adjustable computing resources, serverless computing introduces a revolutionary approach that obviates the need for manual intervention in the management of physical server infrastructures. This study, grounded in an array of practical implementations, unveils the multifaceted benefits of serverless computing, including substantial cost reductions, remarkable scalability improvements, and accelerated processing speeds. Furthermore, the investigation expands its horizon to encompass an exploration of serverless computing’s impact on a wide spectrum of disciplines, ranging from space and terrestrial experiments to atmospheric research, and extending into the burgeoning fields of quantum computing and mathematics. Through a meticulously designed series of experiments within these diverse domains, the research underscores the critical role serverless computing plays in the advancement of cloud computing applications. It sheds light on its far-reaching implications for big data analytics, artificial intelligence, and distributed systems, illustrating how serverless computing is poised to surmount the predominant challenges faced by traditional computing paradigms. By providing a comprehensive overview of serverless computing’s capabilities in facilitating a new era of data processing and utilization, this study contributes valuable insights into its potential to redefine the information technology landscape. The findings underscore the pivotal role of serverless computing in navigating the complexities of the digital age, offering a promising avenue for enhancing the efficiency and scalability of computing applications across various sectors.
Militech
Authors: Laura Chueca Bronte and Jorge Zurdo Izquierdo (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Architecture and Degree in Videogame Development (UCM) co-advised with David Pacios Izquierdo.
Description: This research presents the development of a distributed architecture, integrating serverless technology and Amazon’s Sagemaker with Artificial Intelligence, aiming at the efficient processing of 3D printed parts for both defense and general applications. This study exploits an experimental 3D convolutional network, to explore the advancements in automated part slicing methods. Furthermore, slicer cutting mechanics of printing files without visual tools, purely relying on coordinates are also being developed. These tools are exported to serverless architectures to leverage the extreme parallelization of AWS Lambda functions. The paper will present the conclusions and results derived from these implementations, offering a novel perspective in the field of 3D printing and AI-driven process optimization.
Construct
Author: Pablo Ezquerro Moya (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Architecture (UCM) co-advised with Juan Carlos Fabero Jiménez and David Pacios Izquierdo.
Description: This work explores the development of a serverless system for generating network topologies using machine learning techniques, specifically through the use of YOLO models. The system leverages object recognition to automatically convert hand-drawn diagrams into digital formats that can be imported directly into GNS3 for network simulation. By automating this process, the project addresses the cumbersome and time-consuming task of manual network configuration, potentially revolutionizing network design practices in educational and professional settings. The implementation uses AWS Lambda to handle processing, providing a cost-effective and scalable solution.
Ice-Wall
Author: Santiago Mourenza Rivero (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Double Degree in Computer Science and Mathematics (UCM) co-advised with Juan Carlos Fabero Jiménez.
Description: This work will approach issues related to cybersecurity in order to create an artificial intelligence-based model that assists in detecting and stopping network attacks. To achieve this goal, a dataset will be used to train a model that identifies the type of the attack occurring, enabling the selection of an appropriate post-processing method to stop said attack.
Space Descent and Landing Simulation
Author: Daniel Ruiz Figueroa (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Video Game Development (UCM).
Description: This is a Space descent and landing simulation developed in Unity, where users can experiment spacial conditions attempting to land a spacecraft successfully on different celestial bodies such as Mars or the moon, and also with recognized ships such as Viking Lander o Lunar Module. The simulation gives you the possibility to experiment with different physical values such as gravity, winds, weight of the ship, fuel or user control. Assets are managed through a cloud data storage system.
Magic: The Serverlessling
Author: Rodrigo Tobar Guillén (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Video Game Development (UCM) co-advised with David Pacios Izquierdo.
Description: Magic: The Serverlessling is an online multiplayer game based in the popular TCG Magic: The Gathering. The internal structure of the game has been totally developed using serverless computing, creating a cost efficient system that will act as a case study of this approach, providing insight about the feasibility of this technology as a game/application development tool.
2022-2023
FDISat: FDI’s Satellite Imagery Acquisition Node
Author: César Falcón Gómez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Architecture (UCM) co-advised with Juan Carlos Fabero Jiménez.
Description: Throughout the day several meteorological satellites pass in a low earth orbit at an altitude of 850km above the Faculty of Informatics and our position. Of all of them, there are four (NOAA19, NOAA18, NOAA15 and METEOR-M2) that broadcast in the 137MHz band and are freely available since communications are not encrypted. At present, there is affordable equipment to capture and decode the images, as well as an endless number of free and open source software applications. With all this, this final degree work will be based on a system that is activated when there will be a pass of any of the satellites NOAA19, NOAA18 and NOAA15, above our Faculty of Computer Science, capture the entire pass, decode it and through a web page remotely can be displayed on the information screens of the faculty, all in a system of few resources such as a Raspberry Pi Model 3B.
Cust-OTEA
Author: Samuel Antonio Eugercios Nevado (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Architecture (UCM) co-advised with David Pacios Izquierdo.
Description: This work aims yo protect PDF documentation under secure and invisible watermarks, to prevent its theft and fraudulent use by websites illegally. The project covers The creation if invisible and secure watermarks and the modification of document metadata, along with The processing of all operations through Cloud computing.
CONFIGUPAR
Author: Raúl Caballero Girol (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM) co-advised with Enrique Molinelli Fernández (CEHIPAR-INTA).
Description: In modern ship design, the calculation of the ship's drag is one of the keys to the success of the design. If the resistance is poorly estimated, a very high investment can be made in the construction of the ship and discover, a posteriori, that it does not reach the minimum parameters we had predefined, such as the ship's top speed or maximum fuel consumption. Failure to reach these values could mean a very important economic disaster for the shipbuilding company. Currently the estimation of this value cannot be calculated mathematically so different statistical and empirical methods are used to obtain it. CONFIGUPAR intends to use machine learning methods to predict this value. This could lead to significant cost savings prior to construction, since a simpler and more reliable method than the current ones would be obtained and, therefore, more economical.
2021-2022
Improvement of QoS for Multimedia Platforms
Author: Dámaso González Pino (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Computer Science (UCM) co-advised with Francisco Javier Rodríguez Pérez (UEx).
Description: This is a collaborative project between the Complutense University of Madrid and the University of Extremadura, which aims to improve communications in data transfer. The objective of the work is to analyze ways to optimize the QoS in multimedia platforms. The hypothesis to be evaluated is whether by bringing the content that users request closer, they would be accessed faster, the network would be decongested and the number of requests against the main servers where that data is hosted would be reduced, or if, on the contrary, bringing the content closer might not be an optimal alternative. For this reason, we have carried out the following tests: (1) comparison of the technical requirements in different multimedia platforms, (2) analysis of the perception of users through surveys on these services, (3) tracing of routes to physical servers and (4) simulation of different network topologies with different routing protocols. With the tests carried out, we have been able to verify that there are various alternatives to improve the quality of these services.
AI-enabled university degree prediction and recommendation chatbot
Author: Salvador Moreno Sánchez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Digital Linguistics (UCM) co-advised with David Pacios Izquierdo.
Description: This study seeks to develop an automated tool that provides a response to academic and vocational guidance activities, and therefore proposes a chatbot for predicting and recommending university degrees, subject to Artificial Intelligence. As a result of the project, a complete analysis, development and real test of a conversational assistant implemented in Telegram and deployed from the cloud is presented, in which data analysis, natural language processing and machine learning tasks are tackled for its construction. All of this natively and following the open source philosophy.
Distributed Cloud Gaming Pipeline
Author: Laura Mazzuca (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Computer Science (UCM).
Description: There are still many challenges posed to the optimization of resources consumption in Game Engines, especially with the objective of deploying them on the Cloud to provide a new category of Cloud service named Gaming as a Service. Even though game engines are intrinsically modular, very rarely research focuses on building a cloud first architecture due to the strict requirements of efficiency to deliver a good QoE that are easily lost adding delay stemming from networking. The Distributed Cloud Gaming Pipeline architecture proposed in this work tries to take advantage of the developing technologies in cloud computing to be able to distribute the game engine along the cloud continuum exploiting a Middleware featuring a context aware orchestrator.
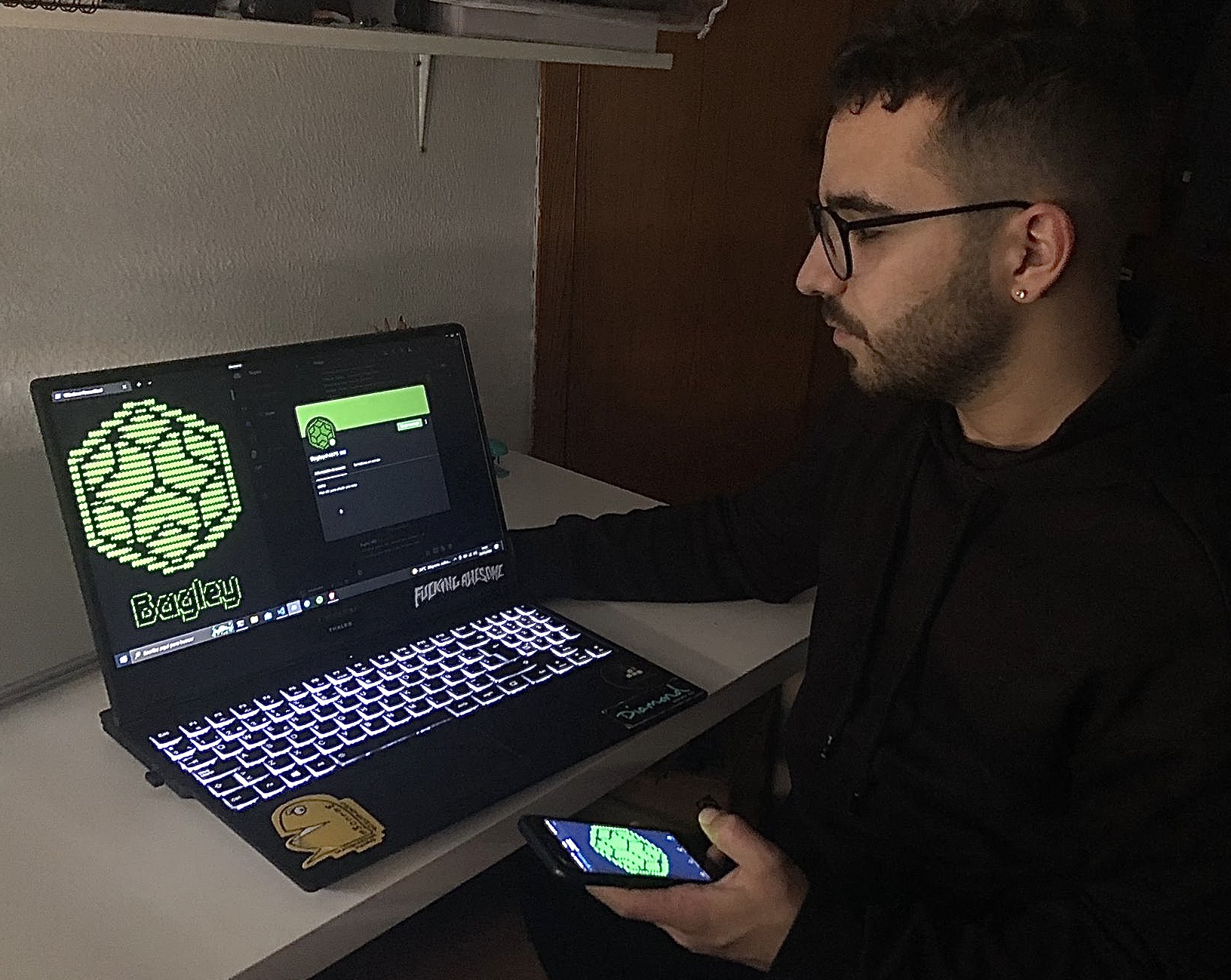
Bagley
Author: Víctor Fresco Perales (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM).
Description: Bug Bounties are monetary rewards that companies pay to independent security researchers when they successfully find and report an exploitable vulnerability. A bounty for a critical vulnerability in a big company can reach the equivalent to a year’s salary in Spain, and this amount is not defined by the complexity of the bug, but by the impact of it. This means that very simple to find and exploit bugs that affect critical infrastructure can report a very big amount of money if the person who finds it is in the right place, in the right moment. The goal of this project is to build and maintain an automated tool that runs on its own, in a Virtual Private Server and is able to perform reconnaissance and detect these simple vulnerabilities in a target. It also implements a communication interface over Discord, so that the researcher can operate it at any moment with any device and find out immediately if something is discovered, making it the perfect tool for assisting bug hunters.
Applied speech emotion recognition on a serverless Cloud architecture
Author: Robert Farzan Rodríguez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM).
Description: The idea of this work intends to be an “emotion tracking system” that couples serverless technologies along with AI and a simple end-user GUI app that anyone could use purposefully to track their own voices in different situations - during a call, a meeting etc. - and get a brief summary visualization of their emotions across time with just a quick glance.
CAL
Author: Marina Jiménez Garrido (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM) co-advised with Juan Carlos Fabero Jiménez.
Description: CAL is a system for contactless booking and inventory for libraries. It consists of multiple devices placed on the shelves of each bookshelf throughout the library that communicate with a module installed in the main computer of the library. Every book must have a RFID tag and it must be registered in the library program. Each device contains an ESP32 microprocessor, a WiFi module, a RFID antenna and a control program. Each device reads the RFID tags at their reach periodically and they send them to the installed module on the main computer of the library. The devices are registered in this module including their location on the shelf and bookshelf. The control module updates a data base with all the books of the library with this information. This way the actual inventory of the books of the library and their actual location is maintained. The booking system of the library connects to a web service installed in this module to be able to consult if certain book exists and its location at any moment.
DataSekura
Author: Alberto López Cervantes (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM).
Description: The security of the user’s files has been, and still is, one of the most important aspects compromised by cybercrime. This is a consequence of computers becoming a fundamental tool in people's lives. In parallel, mechanisms to violate the security measures of these computers and access sensitive information within them have been created. For this reason, the development of tools that can provide a strong and solid protection to files which the user considers important has become a task of vital importance. Within this context, DataSekura was created to protect information stored both in the local file system and in Cloud services by using encryption techniques. The application allows the user to select a local directory or a folder in the cloud and encrypt it with a very high level of security, entirely using open-source technologies.
Serverless architecture for data processing and detecting anomalies in MARSIS instrument
Author: David Pacios Izquierdo (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Computer Science (UCM).
Description: This work produced a serverless modular architecture for proccesing data from the MARSIS instrument (ESA Mars Express Mission). In particular, ionogram analysis is performed for a perfect detection of anomalities in the Martian athmosphere.
Outreach: Twelfth Moscow Solar System Symposium (October 11-15, 2021)
2020-2021
Development and Optimization of Cloud Computing Applications for Bioinformatic Analysis of massive Sequencing data (RNA-seq and RAD-seq) of woody Forest Species
Author: Fernando Mora-Márquez (Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Spain)
Context: PhD Thesis in Advanced Forest Research (UPM), co-advised with Unai López de Heredia.
Description: High-throughput massive parallel sequencing (Next-Generation Sequencing - NGS) yields millions of DNA fragments sequenced quickly and in parallel from multiple individuals. The use of methodologies based on massive sequencing is beginning to be used routinely in forest genetics to determine the genome structure of woody plant species in an evolutionary and comparative framework, the function of genes and regulatory regions and the relationships of genotypes with phenotypes. Woody plant species present intrinsic peculiarities to their genomes and their vital and reproductive cycles, and a general lack of quality genomic resources, which imply to develop and optimize algorithms, workflows and applications specially adapted for the bioinformatic analysis of large-scale massive sequencing data. This PhD Thesis aimed the development and performance assessment of a computer system that offers a global and unified platform for the analysis of experiments of two of the most popular NGS techniques (RNA-seq and RAD-seq) and the functional annotation specifically oriented to woody plant species in an efficient way, using cloud computing as a hardware resource provider.
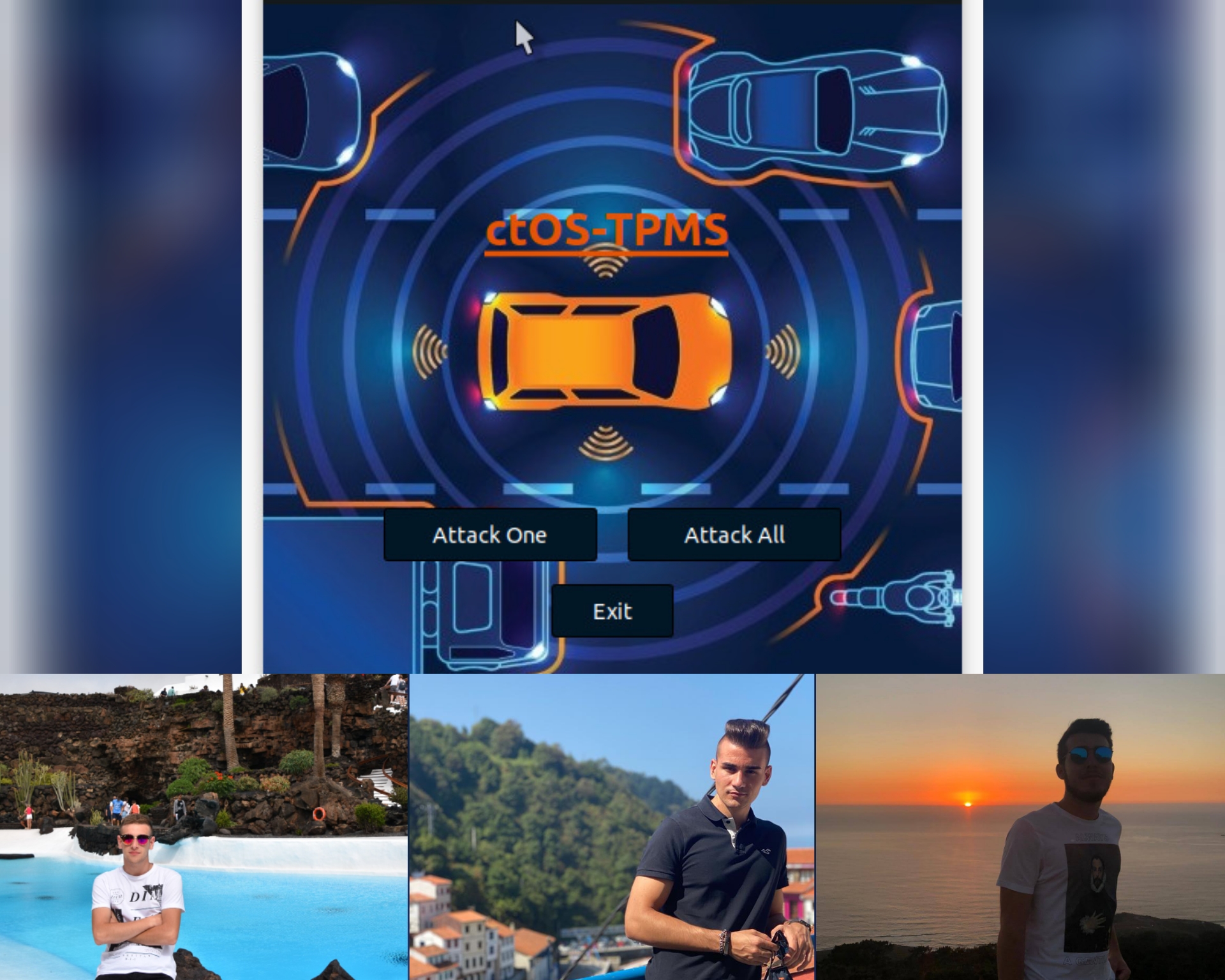
ctOS-TPMS
Authors: Jorge María Martín, Alberto Rodríguez Fuentes and Martín García Fuentes (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), co-advised with Juan Carlos Fabero Jiménez.
Description: Nowadays the safety elements of vehicles have become key to reduce the number of accidents and possible injuries. Among all the existing security systems, this project is focused on the TPMS, the tire pressure monitoring system which is mandatory in all new vehicles since 2014 with category M1. This system provides information about the state of the tires and connects withthe main system of the vehicle by radio signals, which send different types of alarms based on the received data for temperature and pressure. These signals are sent without any encoding, so with the appropriate tools, it is possible to receive and modify them in order to confuse the vehicle's onboard computer. This project explains the process to successfully manipulate the signal and provides a working prototipe.
YouRuleYouRole
Author: Álvaro Rodríguez-Peral Bustos (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Video Game Development (UCM).
Description: Playing a tabletop role-playing game can be quite difficult for numerous reasons. On many occasions it is difficult to coordinate so many people to be able to play a game (taking into account that a minimum of 3 people are needed to be able to play, being the recommended between 4 and 6), other times there is no suitable place where to meet to play and there are also on other occasions barriers such as the difficulty of certain game systems, which may require different rolls with different types of dices (4, 6, 8, 10 or 20 faces) to sometimes solve something as simple like a simple sword blow. YouRuleYouRole intends to overcome these limitations by providing a virtual space in which it is possible to meet with friends to celebrate role-playing games through a simple system of rules, providing the figure of the master with a pseudo video game engine where they can develop their games without the need to know how to program and where the players will be able to intuitively see the effects of their actions in the game without the need for long procedures and checking complicated tables.
2019-2020
SOL-BAM
Author: Enrique Miguel Torrijos Gabriel (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM).
Description: The Banco de Alimentos de Madrid (BAM) is a NGO that seeks to deliver food to anyone who can’t afford it. This organisation has a lot of changes in personnel because the vast majority of them are volunteers, making very difficult managing the Bank’s internal process. The System for Optimized Logistics for Banco de Alimentos de Madrid (SOL-BAM) is a solution to this problem. People can connect through a browser and manage all this information that wasn’t controlled effectively before.
Ámesos
Authors: Mario de los Santos Sainz and Raúl Fernández Guardia (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Video Game Development (UCM).
Description: Ámesos is an application capable of deploying and closing on-demand game servers in data processing centers closest to clients, which will cause, when clients connect to these servers, a decrease in ping that will lead to a better gaming experience for the players.
Sentinel
Author: David Pacios Izquierdo (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM).
Description: This work aims to detect the incomplete flicker and relate it to pathologies for their prediagnosis, such as: allergic conjuntivitis, dry eye and pathologies linked to the ocular fatigue. The project covers the ad-hoc frame production using 3D scanning and printing technologies, along with data processing using cloud clomputing.
Outreach: "Hoy por Hoy" (Cadena SER) and Concurso Universitario de Software Libre
2018-2019
Deployment of Blockchain technology in Serverless infrastructure
Author: Daniel Ortiz Sánchez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Computer Science (UCM).
Description: This project deals with two new technologies that, a priori, should not have anything in common. On the one hand, we have the blockchain technology. At a time when corruption and transparency are two issues that are present every day, studying a technology that treats them fully becomes very stimulating. On the other hand, the author’s career has led him to work building web applications, architectures and microservices. Encouraged by the director of this project, the more he discovered about cloud platforms and possibilities such as lambda functions, the more he believes that the future is to go in that direction. It was necessary to verify if both technologies could be combined and benefit.
Chronos
Authors: Javier García Lorenzo and Carlos Lozano Casado (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM).
Description: Chronos is an app to help to students and teachers to plan their academic year. A few days before enrollment period, the students start to decide which subjects will study that year. The students agenda, the subjects they want to study and their schedule can make this task very difficult. Chronos has been developed to make this task much easier. The student only have to indicate their availability and what subjects they want to study. The app will check the combination and tell the student if it is possible or not. The teachers will report how many credits they would want to teach and up six subject ordered my preference. When Chronos receives the teachers' selection order, it will assign the subjects according to their preferences, the credits indicated and the subjects' vacancies.
2017-2018
Cloud PIE
Authors: Rodrigo Crespo Cepeda (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Computer Science (UCM).
Description: It has not been that long since the creation of the first computers and communication networks. However, in the recent years, the rapid evolution of technology and its great acceptance by the general public, has motivated the creation of infrastructure as a service in the cloud providers. The growing mass of cloud computing services has caused infrastructure providers to experience a shortage of resources that affects consumers directly, making it necessary to create SLAs for assurance. This has influenced the increase of research in new techniques for resource use optimization. Cloud PIE is a proactive and intelligent ecosystem in the cloud, whose main goal is to ensure the availability of resources for cloud services in the most efficient way possible. For this purpose, it is composed by a series of modules, in the form of microservices, that allow it to make intelligent decisions about the possible mutations that must be applied to the system. Cloud PIE uses a rules based system for decision making, infrastructure management and hardware and software data monitoring tools, as well as a module that allows it to evolve its knowledge, to make more accurate and adjusted decisions based on the deployed services. In this way, Cloud PIE becomes an effective technology for automated, intelligent and proactive management of cloud infrastructure resources for heterogeneous services, as a innovative idea to solve the mentioned problem.
Cypher as a Service
Authors: Álvaro Gómez-Arevalillo and Kurosh Dabbagh Escalante (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM).
Description: Nowadays is hard to think about a future of Computer Technology without the concepts of cloud computing and cyber security. Cloud gives a greater storage capacity and an enormous processing power in comparison with which we could obtain using our personal computer. Cyber security, through techniques such as encryption, keeps our sensitive data and communications from the reach of cybercriminals. The aim of this project is the creation of an encryption service in the cloud through an API REST that brings the encryption closer to both developers and people without technical knowledge. In this way developers will have a simple way to encrypt their files and communications regardless of the language they are coding and without need to invest a lot of time to understand the intricacies of encryption. Non-expert people would be also allowed to use that service without the worries about the limits of knowledge in the field of encryption they could had.
IDNet
Authors: Juan Más Aguilar and Lorenzo de la Paz Suárez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM).
Description: Recent events have triggered many concerns about Big Data and the security of our private data. This situation has maximized the already existing discussion between Privacy and Security. Personally, we think another concept should be added to this discussion: Efficiency. Why? Because Big Data has come to stay; side by side with many other technologies that treat our data to discover patterns in our lives that many of us are not even aware of. Are this technologies dangerous for people? Not necessarily. Many institutions such as medical or scientific researching entities could get advantage of this data to transform our society for the better. But this roadmap clashes directly with one of the original concerns: Security. That is why IDNet has been created. A first aproximation to fuse the three concepts. IDNet could allow institutions to communicate worldwide while having personal data protected and achieving great levels of efficiency.
Internet was not made to be safe, but IDNet is.
2016-2017
Mutokamwoyo Cloud
Authors: Juan Montiel Cano, Alba Montero Monte, Sergio Semedi Barranco and Adrián Martínez Jiménez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), co-advised with José Manuel Velasco.
Description: Mutokamwoyo Cloud finds a way to use the new Cloud computing paradigm for volunteer purposes. This project aims to develop and deploy a light cloud system customized for a populated area in Africa. Nowadays communications and internet are essential, the project's final goal lies in providing access to knowledge on useful topics like general education, medicine or entertainment to those people who don't have the possibility.
Outreach: Concurso Universitario de Software Libre.
SmartCity Overseer
Authors: Javier Villareal Rodríguez and Christian González Jiménez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), co-advised with José Manuel Velasco.
Description: SmartCity Overseer is a control panel that allows to manage the services of the city in an efficient way. This is achieved by obtaining information in real time of the city's conditions, both real and virtual. Information about incidents help the City Hall to make decisions through Big Data analisys of tweets. It also provides a telegram bot that provides any relevant information on the city's condition.
Deployment and Migration of Business Services in the Cloud
Author: Bartosz Ignaczewski (Lodz University of Technology, Poland)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), Erasmus Programme.
Description: Cloud solutions in business are nowadays getting more and more popular. Many companies decide to deploy their applications in the cloud or migrate them from their non cloud based solutions. It allows them to focus on funcionalities and turn over the work connected with software distributed architecture and scalability issues to cloud providers. However, they still need to spend a lot of time on building the whole cloud infrastructure. The goal of this work is to create an integrator that makes the communication with cloud provider(s) (Amazon in this case) as easy and quick as possible, aiming to be used even by non-technical users. It supports the full process of application deployment and termination along with cloud-based database management, what drastically lowers the time needed to set up the infrastructure.
2015-2016
Application Execution Optimization in Heterogeneous High Performance Computing Environments
Author: Richard M. Wallace (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: PhD Thesis in Computer Architecture (UCM), co-advised with Daniel Mozos.
Description: High performance computing systems are used as singular, cluster, or cloud resources requiring software to be written treating these resources as homogeneous compute platforms regardless of heterogeneous components. As such, developers rely on source language pragmas, inter-process communication libraries, compiler directives, and link- loader directives to control programs executed on the appropriate computational processor. In practice specific manual tuning must be done. Current work with auto-tuners shows that there is little attention to federated, distributed methods of determining the optimal mapping of execution units across cloud-deployed computational platforms. This research concentrates on models of computation and allocation methods for executable components to be allocated across federated, distributed computation systems constructed from homogeneous and heterogeneous compute elements.
FingerPay
Authors: Robert Slavi Marinov, Pablo Fernández Grado and Francisco Javier Sánchez Platero (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), co-advised with José Manuel Velasco and Eva Ullán.
Description: This project aims to provide a disruptive way to pay in small businesses being convenient for both the buyer and the seller. Fingerpay is a new secure payment method that exclusively relies in the fingerprint without needing extra devices such as smartphones. Also, security is increased by distributing the user information (data, fingerprints) with cloud computing federation methods.
Translogistic
Author: Piotr Rzeznik (Lodz University of Technology, Poland)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), Erasmus Programme.
Description: Logistic companies need smart and fast tools to be competitive players on the transport market. TransLogistic system was designed to fulfil all necessary needs in field of tracking the freightage. Thanks to that client has an ability to follow his shipment order in real-time by the map visualisation (route and location points are being marked). The system is able to register different types of shipment and can be easily used for tracking the current status of parcels and updating it. User scans QR code, which is placed on the container or package, by the mobile device in order to read freight’s identification number and is able to view the current location on the specially designated website. Current route is automatically generated from the logged records. All the location points which belongs to the company are stored in the database amongst the orders and packages' details. Requests are served by the REST web service.
CloudBotNet
Authors: José Luis Góngora Fernández and Abdallah Fallaha Sabhan (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), co-advised with José Manuel Velasco.
Description: Cybersecurity is a field that everytime is more present in our lives with the advance of the technology. Governments, military, corporations, financial institutions, hospitals and other businesses collect, process and store a great deal of confidential information on computers and transmit that data across networks to other computers. With the growing volume and sophistication of cyber attacks, ongoing attention is required to protect sensitive business and personal information, as well as safeguard national security. In the future almost everthing is going to be computer-based so with the advance of the technology new threats will appear, more dangerous and sophisticated. The approach of this project is to demonstrate that with a few knowledge of network security, cloud computing and some coding lines it is possible to implement a powerful attack tool that could represent a serious danger for the integrity and confidentiality of users and institutions.
NetworkSafeBox
Authors: Rodrigo Arranz López and Rafael Delgado Meana (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), co-advised with José Manuel Velasco.
Description: At present we are connected the Internet permanently either at home or at work. Anyone can access the Internet quickly and easily from almost any electronic device to search for information, play games, watch multimedia content, etc. The problem is that cyber criminals are taking advantage of people who do not care about their network security. Cyber criminals usually have extensive computer knowledge, but most people have little knowledge about computer security. How can these people defend themselves from cyber criminals? To solve this problem we are developing the project NetworkSafeBox. NetworkSafeBox adds a layer of security to your Internet connection. Without much knowledge about computer security a user can control the incoming and outgoing traffic through a web interface in a few clicks. NetworkSafeBox creates a network of virtual machines that controls Internet connections based on user needs and protects against malicious access to your home or work network.
2014-2015
PHYLOGENY-EVOLUTION-CLOUD
Author: José María González Alba (Hospital Ramón y Cajal, Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (ISCIII)
Description: The central idea of evolutionary theory is that species are related through a history of common descent, any study of DNA sequences sampled from different species or from different individuals in a population is likely to start with a phylogenetic analysis. Phylogenies are used in almost every branch of biology and become an indispensable tool for genome comparisons. The quantity of sequence data produced by Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) technologies and the complexity of the questions in evolutionary biology pose great statistical and computational challenges. Bayesian Evolutionary Analysis by Sampling Trees (BEAST) is a cross-platform program for Bayesian analysis of molecular sequences orientated towards time-measured phylogenies and it is used as a method of reconstructing phylogenies for testing evolutionary hypotheses without conditioning on a single tree topology. The computational speed of the Bayesian method is highly data-dependent. The separate analysis is useful for studying the differences in the reconstructed gene tree; however, it is inefficient for estimating the common phylogeny that underlies all genes. The aim of the present project is to evaluate which is the best combination of CPU, memory, storage, and networking capacity to use in terms of execution time and costs process for Bayesian evolutionary analysis of large genome datasets in a reasonable time frame.
Ender
Authors: Iratxe González, Sergio Carvajal, Javier Serrano, Todor Velikov and Daniel García (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), co-advised with José Manuel Velasco.
Description: IT-Security is one of the biggest concerns in our nowadays society. Fast development and growth of new technologies which depend on the Internet has made people more concerned about the security of their data, increasing the fear the this data could be easily compromised. One of the actions that are being taken against security flaws is the education and training of experts. This effort is focused on guaranteeing the integrity and confidentiality of the cyberspace and the people who use it. The goal of this project is to create a framework that will allow people to train themselves in cibersecurity. In order to achieve this goal, Ender consists in a cloud where digital warfare scenarios are deployed. These scenarios have different goals and require different attack skills. The user will be able to use his own computer and tools to complete the proposed challenges.
3D visualization and analysis for Big Data using cloud computing GPUs
Author: Pedro Rodríguez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: M.E. in Computer Science (UCM), co-advised with José Manuel Velasco.
Description: The presence of technology in our day to day activities, coupled with the reduction in data storage costs, has started the era of Big Data. However, processing and visualizing such quantity of data requires specific software and hardware, and not all the users have the opportunity to access this technologies. On the other side, modern GPUs have very high specifications, and each new generation provides bigger amounts of fast memory and better parallel computing capabilities. The use of this hardware makes easier to work with big amounts of data, however most users lack the specific knowledge needed to work with modern GPUs. Thanks to the newest cloud computing technologies it is possible to provide a web service that will allow every user to analyze, operate and visualize his data as fast as possible using the latest GPU technologies. The web service will get as input the user data, and will provide different ways to work with it. The user will not need any kind of knowledge about the technologies used in the background to work with the data. This project aims to develop a server application capable of analyzing big quantities of data using GPUs specific software. The user will interact with the server application using a browser web application.
CtOS Enabler
Authors: Meriem El Yamri, Rodrigo Crespo and Juan Manuel Carrera (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Degree in Computer Science & Engineering (UCM), co-advised with Eva Ullán.
Description: Smart Cities are, undoubtedly, the near future of technology we approach every day, which can be observed in the profusion of mobile devices among the population, these devices automatize daily life through the use of geolocation and information. Two areas that we intend to unite with CtOS Enabler to create a standard of use that encloses every Smart Cities system and eases the creation of new tools to developers of that kind of software. CtOS provides a low-complexity layer that transforms the interaction between information and positioning in a simple task, thus enabling the possibility of creating a high quality and successful product. The complete functionality resides in the Cloud, allowing its resources to be easily scalable and accessible. The system focuses on qualifying the user to define regions of work where to store information that interacts with their devices when they are within those zones, allowing to perform location-based real time tasks. Also, as an added value, statistical data of service usage is provided to help improve the customer's product. CtOS Enabler is geared for both developers, who can use it as a Platform as a Service (PaaS), or companies, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers, willing to use the API or acting as intermediaries to provide the service to their own customers, focusing on various highly flexible subscription models, according to the functionality required. CtOS Enabler helps to improve the geolocation capacity of any software, such as location limited chats, a smart parking app, or something more complex like a traffic light and bollards control system for law enforcement and rescue bodies in state of emergency.
Outreach: Smart Cities DataFest Hackaton (IBM Prize), #SUPMVC2, Madrid Venture Café, Startup Programme, El Economista, Te Interesa, La Información, Europa Press, Ingenieros, RedEmprendia, El Referente, Servimedia, Discapnet, Diario Siglo XXI, Emes, La Linterna (COPE), InnovaSpain, Emprendedores, Infocalidad, Crónica Norte, Radio 5 (RNE) and Tribuna Complutense.
Personal AnonyCloud
Authors: Alba Moragrega, Alberto González and Sergio Baños (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: M.E. in Computer Science (UCM), co-advised with José Manuel Velasco.
Description: This project attempts to solve some of major problems of using nowadays public networks. On one hand, VPN is used mostly for point to point connections. With Personal AnonyCloud, the user will be able to build a VPN network composed of various relay servers. It also increases network security, as the machines composing the network are owned by the used. These machines can be created on demand using public cloud providers, so they can be replaced in case of intrusion. Besides, Personal AnonyCloud offers an intuitive and simple interface, allowing the use of the tool to almost anyone, regardless of the level of technical knowledge about VPNs and security.
2013-2014
Face recognition security system on public cloud infrastructures
Author: Ramón Pintado (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Research in Computer Science (UCM)
Description: Nowadays security is a key issue in our society. Public places with large numbers of people such as airports, train stations or even crowded social events have security systems with video surveillance. This project proposes two models for the implementation of a security system using the emerging technology of facial recognition and equipped with enough power to handle large amounts of data using public cloud technology. The first model, ready for static scenarios like security booths, cash machines or one-way corridors, provides very accurate results by controlling lighting, pose or expression of individuals analysed. The second model is prepared for dynamic environments, such as IP surveillance cameras, in which environment variables are not controlled, acting as an excellent support system of the first model. These models allow the identification of persons whose photographs are included in the large databases of different security agencies in the world. Additionally, thanks to the wide variety of machines offered by public cloud, based on decision tree model is presented, in which the user can easily determine the number of machines he needs depending on the flow of people, maximum time for the identification and monetary cost he is willing to take; the best performance or maximum power.
RS-ENT-CLOUD
Author: Unai López de Heredia (Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (ISCIII)
Description: Next Generation DNA/RNA Sequencing studies produce big amount of data that need to be analysed with proper computation infrastructure that is not always available for all research centers or universities. Expressional analysis derived from Rna sequencing (Rna-Seq) of forest trees is particularly challenging, because the massive genome length genome (~23.2 Gbp for loblolly pine) and the absence of reference genomes require specific pipelines to obtain sound biological results. The cloud computing paradigm makes economically affordable the implementation of such pipelines. If an algorithm can be made to run efficiently on many loosely coupled processors, implementing it as a cloud application makes it particularly easy to exploit the resources offered by large utility-computing services, such as Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud. The aims of the present project are: 1) to review the tools and pipelines for differential expression analysis using Rna-Seq data; 2) to optimize a pipeline for the analysis of differential expression in non model species with large genomes; 3) to analyse the cost-efficiency of the pipeline in the Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud vs. local systems.
EMS in Cloud
Authors: Alejandra González, Ricardo Champa and Claudia Montero (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: M.E. in Computer Science (UCM), co-advised with Manuel Vázquez (Gobierno de Aragón EMS).
Description: In the world of medical emergencies, every second is valuable. Medical teams have mobility needs, and one way to improve their performance is to take advantage of software applications based on cloud systems. This approach makes protocols and tools available to every team who needs them. EMS in Cloud is a Software as a Service system deployed in multiple platforms. The framework provides an economic solution in the way a cloud system works, providing service and continuing care. Even if there is no internet available, EMS in Cloud offers a mobile client that is able to work offline with most of its functionality.
Outreach: HPCwire.
CloudMiner
Authors: Tomás Restrepo, Juan Arratia and Arturo Pareja (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: M.E. in Computer Science (UCM).
Description: CloudMiner is a project that aims for a better exploitation of the existing hardware, achieving economical benefit through the mining of virtual crypto-currencies. The main idea is to create a cloud-computing resource pool, composed by diverse machines under potentially different architectures. This pool will be monitorized in real-time by the application, enabling the user to start/stop mining at any given point on any of the available machines, also providing information on their current status. Additional options will be available, like adding or removing resources (supported architectures). Artificial Intelligence based on statistics may be used in order to allow automated control of the mining cloud. These statistics are also visible to the user, to aid decision taking.
Outreach: HPCwire.
2012-2013
On-demand secure teleconferencing on public cloud infrastructures
Author: Bernardo Pericacho (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: Master in Research in Computer Science (UCM), co-advised with Ignacio Martín-Llorente.
Description: One of the main handicaps of migrating applications to the cloud is security. Having no control over how our data travels through the Internet and not knowing who has access to them, make users reluctant to adopt a public cloud migration strategy. Communications over the Internet are a concrete example where users may need to communicate in a secure way not susceptible to eavesdropping or interception, i.e. not having a third party to listen in. In this project, two new secure teleconferencing architectures deployed in the cloud are presented, Teleconferencing Secure Cloud VPN Architecture and Hidden Teleconferencing Server Cloud Architecture, to address possible security breaches and attacks in voice over IP (VoIP) communications in an unsafe environment such as the Internet. In addition, a model represented by a decision tree is proposed, in which a user can easily determine which architecture and infrastructure is the one that best fits his needs when establishing a secure teleconference server on a public cloud.
Outreach: HPCwire.
CygnusCloud
Authors: Luis Barrios, Adrián Fernández and Samuel Guayerbas (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: M.E. in Computer Science (UCM), co-advised with José Antonio Martín H..
Description: This project aims to provide virtual lab machines that can be accessed from any available campus PC in which the both hardware and software requirements are minimal. An on-demand and centralized distribution of these services like that proposed by CygnusCloud reduces the effects of budget cuts in education as students could use cheaper computers with less energy consumption. The proposed solution increases the academic progress as it optimizes the use of non-specialized computer labs and reduces costs as it relies totally on open source software.
Outreach: HPC in the Cloud, Cadena SER, Blog, Buenas Noticias (UCJC), Concurso Universitario de Software Libre and Premio Proyecto Fin de Carrera 2012-2013 itSMF.
SmartCloud
Authors: Ailyn Baltá, Javier Bachrachas and César Cayo (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: M.E. in Computer Science (UCM), co-advised with José Antonio Martín H..
Description: SmartCloud is focused on getting the most value out of existing infrastructure, as well as providing a service to UCM researchers or any member of an academic environment. The main idea is to host virtual machines on computers in a LAN that aren't currently in use. These machines don't need to reside in a computer laboratory. Users from the administrative staff also qualify to be in the SmartCloud resource pool. These machines could handle several guest types, which would serve as processing nodes inside a computing cluster or even separate machines for interactive access. One of the approaches is to rely on iPython for providing the researchers access to a powerful Matlab-style web notebook, which would be linked to their Google Drive accounts, sharing their data easily.
Outreach: HPC in the Cloud, Cadena SER, Buenas Noticias (UCJC) and Jornadas de Paralelismo 2013 - Congreso Español de Informática 2013 (Madrid, Spain).
HORADRIM
Authors: Guillermo Marco (Sistemas Genómicos, Spain)
Context: Master in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (UCM)
Description: The environment chosen for this project is Sistemas Genómicos, an SME offering genetic analysis and bioinformatic services. This company had a limited computing environment due to the high demand of running applications. Unfortunately, this demand is not continuous and in the current economic situation scaling through the purchase of new equipment was not a valid option. As cloud computing allows among other things the providing of resources on demand - pay only for what you use - my student saw a great opportunity when his employer signed a partnership with T-Systems. The first objective of the project is to implement a computing prototype that will expand the local cluster infrastructure into the cloud. The second objective is to calculate both economic and computational costs of certain bioinformatic applications in the cloud, in order to maximize the efficiency of the chosen cloud configuration.
Outreach: HPC in the Cloud, Cadena SER and Buenas Noticias (UCJC).
2011-2012
CONSTRUCTOR
Authors: Isabel Espinar, Adrián Escoms and Esther Rodrigo (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: M.E. in Computer Science (UCM)
 Description: This system provides a solution for startups with a low budget that could rely solely on on-demand resources provided by a public cloud infrastructure. A development phase of a given product has specific software requirements that can be restrictive, so the developers need a tool to easily deploy and (re)configure the necessary machines. Also, developers need a standard entry point to the development platform, allowing them to change the context as fast as possible. On the other hand, the startup needs to calculate the exact development cost in order to assign a competitive price to the final product.
Description: This system provides a solution for startups with a low budget that could rely solely on on-demand resources provided by a public cloud infrastructure. A development phase of a given product has specific software requirements that can be restrictive, so the developers need a tool to easily deploy and (re)configure the necessary machines. Also, developers need a standard entry point to the development platform, allowing them to change the context as fast as possible. On the other hand, the startup needs to calculate the exact development cost in order to assign a competitive price to the final product.
Outreach: HPC in the Cloud and Tribuna Complutense
POPULOUS
Authors: Gonzalo Santana Rodríguez (Museo de Ciencias Naturales, Spain)
Context: Master in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (UCM)
 Description: This system aims to understand the effects of climatic elements on the evolution, migration and extinction of species and biodiversity. This is accomplished with complex mathematical models that generate physiologic responses from the studied species according to climatic data. Survival odds for each species are then obtained for a given area. The resulting system verifies if biodiversity in mountains is higher than in other zones or if the climatic change forces species to migrate to other zones where their survival odds are higher. Focusing on a lower level, the parallel application can be executed in both CPU and GPU resources provided by local and cloud infrastructures. For this reason, the OpenCL API was chosen.
Description: This system aims to understand the effects of climatic elements on the evolution, migration and extinction of species and biodiversity. This is accomplished with complex mathematical models that generate physiologic responses from the studied species according to climatic data. Survival odds for each species are then obtained for a given area. The resulting system verifies if biodiversity in mountains is higher than in other zones or if the climatic change forces species to migrate to other zones where their survival odds are higher. Focusing on a lower level, the parallel application can be executed in both CPU and GPU resources provided by local and cloud infrastructures. For this reason, the OpenCL API was chosen.
Outreach: HPC in the Cloud and Tribuna Complutense
2010-2011
RSA@Cloud
Authors: Alberto Megía Negrillo, Antonio Molinera Lamas and José Antonio Sánchez (Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Spain)
Context: M.E. in Computer Science (UCM)
 Description: This system takes the most advantage of Cloud computing and parallel programming in order to factorize very big integers, the real basis of RSA cryptosystem‟s security, by executing different mathematic algorithms like trial division and quadratic sieve. The combination of the Amazon‟s public Cloud infrastructure and private servers has been chosen to achieve this goal, since both make possible to reach optimum results in terms of time and cost. One of the most relevant characteristics of this programming project is that the system has been designed into modules, starting with the simulation software “Forecaster”, whose purpose is to estimate the required processing time and the cost on the Amazon‟s Cloud infrastructure. Another module called “Engine” has been developed to factorize RSA keys thanks to parallel programming properties. Its aim is to connect a server network and to generate and assign computer operations without any interaction by the user. Furthermore, a graphic representation application, “Codeswarm”, has been included as a module into the system, to visualize interactions between servers that perform the factorization task.
Description: This system takes the most advantage of Cloud computing and parallel programming in order to factorize very big integers, the real basis of RSA cryptosystem‟s security, by executing different mathematic algorithms like trial division and quadratic sieve. The combination of the Amazon‟s public Cloud infrastructure and private servers has been chosen to achieve this goal, since both make possible to reach optimum results in terms of time and cost. One of the most relevant characteristics of this programming project is that the system has been designed into modules, starting with the simulation software “Forecaster”, whose purpose is to estimate the required processing time and the cost on the Amazon‟s Cloud infrastructure. Another module called “Engine” has been developed to factorize RSA keys thanks to parallel programming properties. Its aim is to connect a server network and to generate and assign computer operations without any interaction by the user. Furthermore, a graphic representation application, “Codeswarm”, has been included as a module into the system, to visualize interactions between servers that perform the factorization task.
Outreach: HPC in the Cloud, Tribuna Complutense and Jornadas de Paralelismo 2011 (Tenerife, Spain)
2009-2010
GridWay Graphical User Interface
Author: Srinivasan Natarajan (California State University at Sacramento, USA)
Context: Google Summer of Code 2009
 Description: Current Gridway environment does not provide users with a Graphical interface for monitoring and submitting jobs. The changes can be made using GTK+ or The GIMP Toolkit which will use the existing infrastructure of DRMAA API (C bindings). The existing command line interfaces are supported in Graphical User Interface so that users are able to compose, manage, synchronise and control their jobs just by clicking the graphical interface instead of the commands.
Description: Current Gridway environment does not provide users with a Graphical interface for monitoring and submitting jobs. The changes can be made using GTK+ or The GIMP Toolkit which will use the existing infrastructure of DRMAA API (C bindings). The existing command line interfaces are supported in Graphical User Interface so that users are able to compose, manage, synchronise and control their jobs just by clicking the graphical interface instead of the commands.
Outreach: Google Open Source Blog and GridCast